Microservices Data Management
In this article, we are going to discuss Microservices Data Management in order to understand data considerations for microservices. As you know that we learned practices and patterns about Microservices Data Design patterns and add them into our design toolbox. And we will use these pattern and practices when designing e-commerce microservice architecture.
By the end of the article, you will learn how to manage data in Microservices Architectures with applying Microservices Data Design patterns and principles.
Microservices Data Management
Microservices Data Management is really important topic because since we are in distributed systems, we should have a strategy to handle data in several distributed servers.
Every microservice has its own data, so the data integrity and data consistency should consider very carefully.
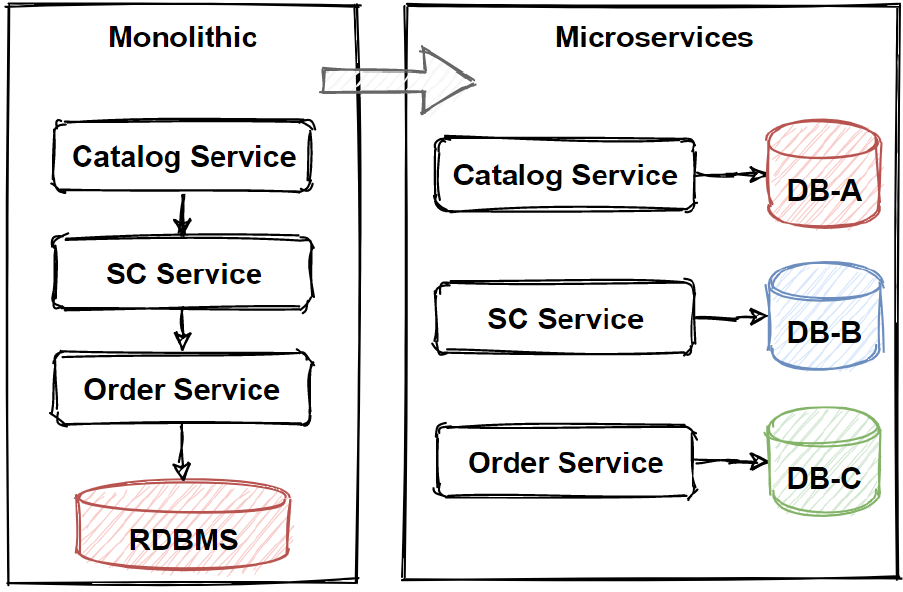
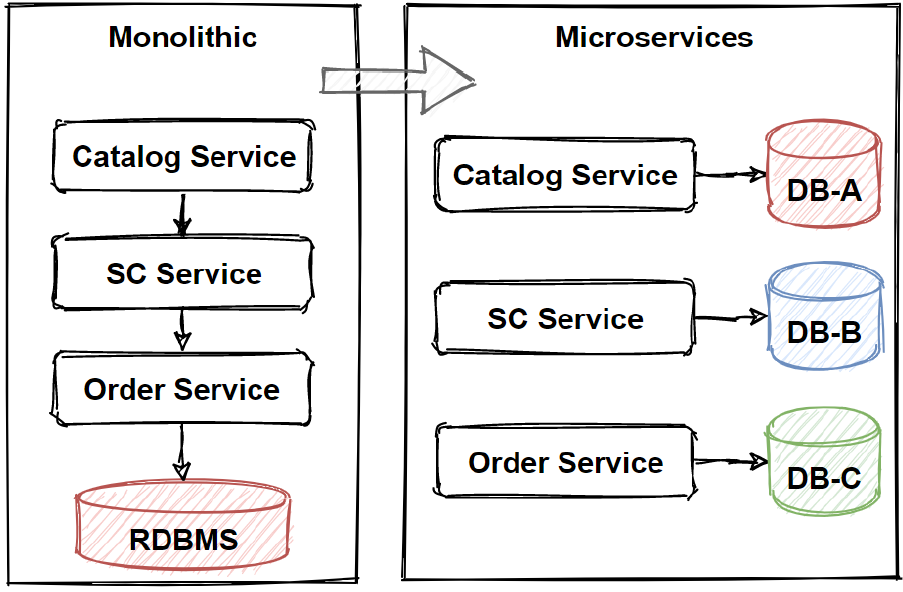
The main principle of microservices data management is that each microservices should manage its own data, we can call this principle as a database-per-service. So that means microservices should not share database with each other. Instead of that, each service should responsible its own database, which other services cannot access directly. It should share data over the application microservices with using Rest APIs.
The reason for this isolation is broke the unnecessary dependencies between microservices. If there is an update on 1 microservices database schema, the update should not be directly affect to other microservices, even other microservices should not aware of database changes. With isolating each service’s databases, we can limit the scope of changes on microservices when any database schema changes happened.
Also by this way, we can pick different databases as per microservices which database can pick the best option. We call this “polyglot persistence” principle.
Polyglot Persistence Microservices
Of course these polyglot persistence principles and separating database comes really heavy Challenges.
Since we have working on distributed systems, managing data is need a strategy. The main Challenges are Duplicated or partitioned data can make problems of data integrity and data consistency.
As you remember that we saw data consistency levels which’s are Strict and Eventual Consistency. So we should decide what is our data consistency level before designing microservices polyglot databases.
In Traditional data modeling is using 1 big databases and Every entity table included in 1 database schema in monolithic applications.
By this way data can not be duplicate and there would not be any data consistency problems due to strict database transaction management.
But In microservices architecture, we have to welcome duplicate datas and eventual consistency of our entity tables.
So how we can welcome duplication and un-consistent data ?
First of all we should accept eventual consistency data in our microservices where it is possible. And we should define our consistency requirements before design the system and if we need to strong consistency and ACID transactions, we should follow traditional approaches. But except this conditional requirements, we should always try to follow eventual consistency data in microservices.
Another way to welcome this features that is using an event driven architecture style. With event driven architecture style, microservices publish an event when any changes happened on data model, so the subscriber microservices consume and process event afterwards in eventual consistency model.
For example, consumer microservice can subscribe events in order to create a materialized view database that is more suitable for querying data. So with separating database in microservices, gives us to abilities to scale independently and able to avoid sigle-point-of-failure of bottleneck databases.
So we should evolve our architecture with applying Async communication or Service Aggregator Pattern in microservices patterns in order to accommodate business adaptations faster time-to-market and handle larger requests.